Mathematics & Computer Science
The Overlake Mathematics and Computer Science Department delivers a rigorous curriculum which provides students with the foundations necessary for college as well as 21st century careers. Critical thinking and problem-solving skills are emphasized throughout our modern, streamlined curriculum. Overlake Math and Computer Science teachers ensure that our students develop an understanding of both the computational skills and theory in all concepts that are presented; we care about not just the “how” in mathematics, but also the “why.”
Mathematics Program
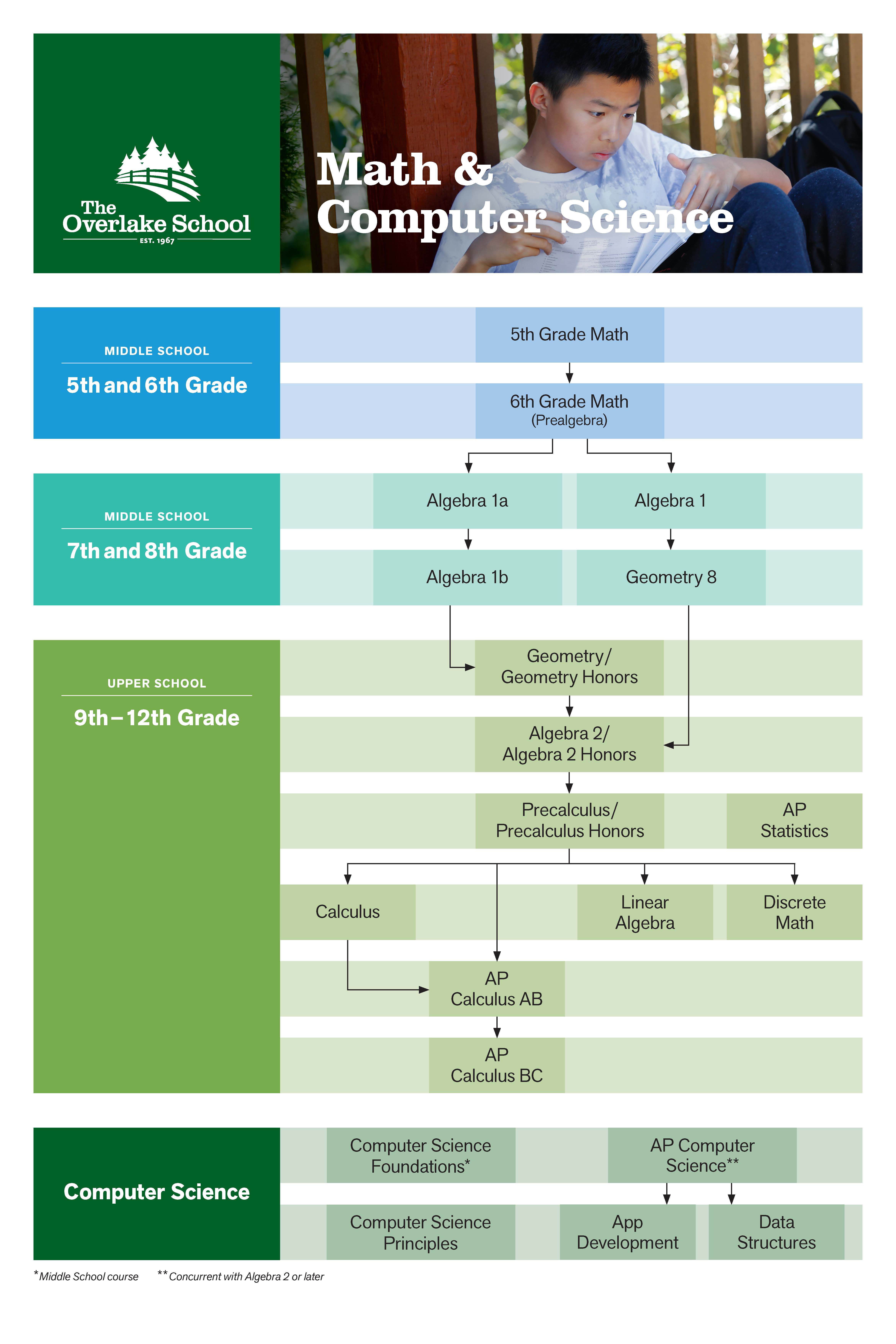
In the Middle School, students work together in a differentiated math classroom as a single community in 5th and 6th grade. In 7th and 8th grade, students are placed into either a 2-year Algebra sequence or a 2-year Algebra/Geometry sequence. All Overlake Middle School students leave 8th grade with a rigorous course in Algebra, and all Upper School students have the opportunity to explore math electives, such as Calculus, Statistics, Linear Algebra, or Discrete Math, by their senior year.
In the Upper School, students will complete (or will have already completed prior to admission) a traditional progression of Geometry and Algebra 2. After this point, students will have the choice between several paths of electives (see Mathematics and Computer Science Department Program Map).
Most of the Upper School Math courses have two tracks: Traditional or Honors/AP. Students are placed in the Traditional or Honors/AP course based upon teacher recommendations as well as student interest. Both tracks cover the foundational material required for success in college mathematics and 21st century careers. Honors and AP (Advanced Placement) courses are intended for students who show special interest and aptitude in math. To earn a placement in an Honors/AP course, students must demonstrate the ability to master concepts quickly, be independent learners, and perform at the top level in prerequisite courses. Honors/AP courses are significantly more challenging than the Traditional courses and demand more from students in terms of homework, independent study skills, and intellectual focus. Placement in the Honors/AP track one year does not guarantee the same placement the following year, and students may transition between the two tracks at any point in the program. Both mathematics tracks are considered highly rigorous by colleges and universities, and students should consider their own interests, course load, and extra-curricular demands when evaluating the pros and cons of each track.
Computer Science Program
There are opportunities for students with any level of experience in computer science and programming to explore and enrich their understanding of these subjects at The Overlake School. “Computer Science Foundations” and “Computer Science Principles” are introductory courses for middle-school and high-school students, respectively. No prior computer science knowledge is expected; in fact, we work to prioritize access for students with no background in programming. AP Computer Science A is offered in the high school, and while no previous programming experience is required, students with any level of background are welcome to take the course. For Upper School students, we also offer a wide array of electives in computer science topics, from mobile app development to data visualization.
For more information on course sequencing, please see the Mathematics and Computer Science Department Program Map.
Graduation Requirements
To graduate from The Overlake School, students must earn a minimum of three credits in core Math courses (Geometry, Algebra 2, Precalculus, Calculus, AP Calculus AB, AP Calculus BC, AP Statistics, Linear Algebra, Discrete Math) in the Upper School. Almost all recent Overlake graduates have completed four or more credits in Math. Students who have completed high-school-level mathematics courses in Middle School (either at Overlake or another school) cannot use those courses towards graduation and must still earn three Math credits in the Upper School. Computer Science courses are not core math courses and may not be used to satisfy the mathematics graduation requirements.
The Overlake School offers a Summer Accelerated Geometry course for current or incoming Upper School students who have completed their first course of Algebra. At this time, this is the only accelerated course we allow for students in our program. This accelerated course does not count towards the graduation requirement and is only intended to allow students to reach advanced electives such as Calculus by their senior year however, students will receive a grade for the course, and it will appear on the student’s high school transcript.
The Mathematics Department believes in the quality of our courses and teachers. Students are not allowed to accelerate or test out of courses once they are placed in an upper school math course. Per school policy, no non-Overlake course credit will be accepted for graduation or acceleration purposes without prior approval from the department chair and Upper School Head. This happens only on exceedingly rare occasions, when a student has extenuating circumstances that prevent them from following our prescribed curriculum.
Students wishing to engage in extra math outside their classwork or over their breaks are encouraged to engage with enrichment programs, either locally or otherwise. Our teachers are happy to provide them with such resources and program listings.
Math 5
All fifth grade students take Math 5. Computation with whole numbers, decimals, and fractions is honed. Keen attention is paid to understanding the effect of operations on quantities in order to develop estimation skills and improve number sense. Students examine algorithms and number composition to enhance understanding of arithmetic properties. Geometry, number theory, ratio, percent, measurement, and pre-algebra concepts are explored through hands-on activities, problem solving, and practice workbooks. Fifth graders also have math labs during which they explore open-ended problems, participate in Math Olympiad contests, and extend their study of topics. Students are regularly prompted to reflect on, prove, or justify solutions during focused discussions. Whole class instruction and smaller skill-group lessons meet varied student abilities. Students continually revisit learned concepts through classroom routines and mathematical games.
Math 6
As students solidify a foundation in decimals, fractions, percent, ratio and proportion, they will become more comfortable with how variables can be incorporated within these concepts. Topics include operations with rational numbers, simplifying algebraic expressions, solving equations and basic geometry. Problem solving techniques and algebraic processes are emphasized throughout the year as students learn to communicate their solutions. Reading, listening, writing, and speaking skills are stressed as students learn to express mathematical ideas just as they would in other subject areas. There is a focus on developing a breadth and depth of mathematical knowledge and skills, with a strong emphasis on conceptual understanding. An equal emphasis is placed on conceptual understanding and skill development – the "why" as well as the "how".
Algebra 7
There are two options for completing Algebra 1: a two-year course and a one-year course. Placement into these courses is done by the middle school math faculty in conjunction with the department head.
This is a rigorous, complete Algebra 1 course. The course content includes solving of linear and quadratic equations, graphing linear equations and inequalities, exponents, radicals, polynomials, systems of equations, and some rational expressions. Because it includes all of the abstract concepts through the solving of quadratics, placement into this course is not solely based on strength in arithmetic, but is also based on evaluation of abstract thinking, academic maturity, and a student's intellectual drive. Applications to science, in addition to other real-world situations, are integrated throughout the course.
Algebra IA
There are two options for completing Algebra 1: a two-year course and a one-year course. Placement into these courses is done by the middle school math faculty in conjunction with the department head.
This course provides exposure to the more concrete topics of Algebra. Students will explore the basic principles and skills of simplifying expressions, polynomials, exponents, radicals, and solving and graphing linear equations and inequalities.
Algebra 1B
Algebra 1A. There are two options for completing Algebra 1: a two-year course and a one-year course. Placement into these courses is done by the middle school math faculty in conjunction with the department head.
This course provides exposure to the more abstract topics of Algebra, building from the foundation created in Algebra 1A. The primary course content will be solving quadratics, graphing linear and quadratic equations, manipulating polynomials, solving systems of equations, and simplifying rational expressions.
Geometry 8
Algebra 7.
This course is for students who successfully complete Algebra 1 by the end of 7th grade. Through independent work, small group work, and guided lectures, students study the properties and relationships of points, lines, planes, circles, polygons and solids in both two and three dimensions. These topics are explored through the integration of arithmetic and algebraic properties along with deductive and inductive reasoning. As students study definitions, postulates, and theorems, they will develop logical and critical thinking skills that transfer to other academic studies. The first semester provides a thorough exposure to using proofs as a means of drawing conclusions. The second semester is more computation and invokes key concepts from Algebra.
Algebra I
This course is designed for students who, for various reasons, have incomplete mastery of algebra entering the 9th Grade. Because algebra is the foundation for most mathematics they will encounter in the future, students who take this course benefit tremendously from securing these important concepts. Care is taken to enrich the familiar curriculum so that the experience feels less like repetition and more like extension. Instruction is varied to suit the needs of individual students. Topics include working with algebraic expressions, linear equations, systems of equations, quadratic equations and factoring, exponents, radicals, inequalities, and graphing. Applications, projects, and other special topics may be incorporated throughout the year at the instructor’s discretion.
Geometry
Proficiency in Algebra
The purpose of the traditional full-year course in Geometry is twofold. It is important that students learn the properties and relationships among geometric figures. Primarily, however, the study of geometry provides fundamental insight into how an axiomatic system works. Development of logical and critical thinking skills and communication with precise language and symbols is emphasized. Special attention is given to writing sound mathematical definitions, formulating reasonable postulates, and proving claims about geometric figures. Both the honors and the regular level classes provide review of algebraic concepts throughout the year in preparation for Algebra II.
Honors Geometry
Proficiency in Algebra and current teacher's recommendation
The purpose of the traditional full-year course in Geometry is twofold. It is important that students learn the properties and relationships among geometric figures. Primarily, however, the study of geometry provides fundamental insight into how an axiomatic system works. Development of logical and critical thinking skills and communication with precise language and symbols is emphasized. Special attention is given to writing sound mathematical definitions, formulating reasonable postulates, and proving claims about geometric figures. Honors-level students are expected to achieve a high degree of mastery and be able to work independently. Advanced topics may be integrated into the honors course at the discretion of the instructor. Both the honors and the regular level classes provide review of algebraic concepts throughout the year in preparation for Algebra II.
Algebra II
Proficiency in Algebra and Geometry
This course is designed to greatly expand students’ understanding of functions and to broaden the algebraic skill set. Students explore polynomial, exponential, logarithmic, rational and radical functions as well as special functions and conic sections. Students deepen their understanding by investigating the inverses of functions. Properties and evaluation of functions, techniques in problem-solving, and inequalities are addressed throughout the year. All of the topics in this course are explored both analytically and graphically, with and without the aid of a graphing calculator. Both honors and regular Algebra II will address a core curriculum necessary to the study of Precalculus.
Honors Algebra II
Proficiency in Algebra and Geometry, and current teacher's recommendation
This course is designed to greatly expand students’ understanding of functions and to broaden the algebraic skill set. Students explore polynomial, exponential, logarithmic, rational and radical functions as well as special functions and conic sections. Students deepen their understanding by investigating the inverses of functions. Properties and evaluation of functions, techniques in problem-solving, and inequalities are addressed throughout the year. All of the topics in this course are explored both analytically and graphically, with and without the aid of a graphing calculator. Honors-level students are expected to achieve a high degree of mastery and be able to work independently. Advanced topics may be integrated into the honors course at the discretion of the instructor. Both levels of Algebra II will address a core curriculum necessary to the study of Precalculus.
Precalculus
Proficiency in Algebra II and Geometry
In the fall, students gain broader and deeper understanding of polynomial, rational, exponential, and logarithmic functions by further investigating their properties and applications. In the spring, a thorough study of trigonometric functions completes the skill set necessary for the study of calculus. Both honors and regular Precalculus will address a core curriculum necessary to the study of Calculus.
Honors Precalculus
Proficiency in Algebra II and Geometry, and current teacher's recommendation
In the fall, students gain broader and deeper understanding of polynomial, rational, exponential, and logarithmic functions by further investigating their properties and applications. In the spring, a thorough study of trigonometric functions completes the skill set necessary for the study of calculus. The honors-level class will apply skills to more difficult, multi-stage problems and move at a faster pace. Honors-level students are expected to achieve a high degree of mastery and be able to work independently. Advanced topics may be integrated into the honors course at the discretion of the instructor. Both levels of Precalculus will address a core curriculum necessary to the study of Calculus.
AP Calculus (AB)
Precalculus and current teacher’s recommendation
The workload, pace, and content of this course is comparable to a college-level calculus course covering limits, continuity, differentiation, and an introduction to integral calculus. Topics in differential equations are also introduced. The College Board AP Calculus AB exam is administered nationally by all participating schools on a predetermined date in May. The College Board website provides the exam date and detailed description of the curriculum, which must be covered in its entirety. Students should expect a high degree of independent learning. Some colleges and universities offer college credit or advanced placement to students passing the exam at a high level. Students are encouraged to investigate these possibilities.
AP Calculus (BC)
Calculus and current teacher’s recommendation
First-year concepts of differentiation and integration are extended to polar, parametric, and vector functions. Students master new methods for evaluating limits, evaluating integrals, and solving differential equations. Series and tests for their convergence as well as power series and polynomial approximations are studied. The workload, pace, and content of this course is comparable to a second or third semester course at colleges and universities.
AP Statistics
Algebra II
The purpose of the AP course in statistics is to introduce students to the major concepts and tools for collecting, analyzing and drawing conclusions from data. Students are exposed to four broad conceptual themes:
- Exploring Data: Describing patterns and departures from patterns
- Sampling and Experimentation: Planning and conducting a study
- Anticipating Patterns: Exploring random phenomena using probability and simulation
- Statistical Inference: Estimating population parameters and testing hypotheses
Successful AP statistics students have good quantitative reasoning, good reading comprehension, clear written communication and consistent study habits. Students will be challenged to think critically about data, to use statistical methods with a deep level of understanding, and to write persuasive responses to real-world questions. A graphing calculator will be the student’s constant companion.
AP Computer Science
Algebra II
AP Computer Science covers the course content defined by the College Board's AP curriculum and prepares students for the advanced placement exam in May. The course teaches the Java programming language and reviews and elaborates on the fundamental methods of object-oriented programming. Much of the material is based on the implementation and analysis of common data structures including arrays and array lists. Basic algorithms for sorting and searching are presented and their asymptotic behavior is analyzed. Students enhance their program design, implementation, testing, and debugging skills through frequent programming projects. Finally, they gain experience reading, understanding and modifying a substantial pre-existing program.
View the College Board AP Computer Science Course Description.
Contact
Rachel Vale
Mathematics Department Chair
rvale@overlake.org